lv shunt borstreconstructie | A Left Ventricular–to–Right Atrial Shunt in a Patient With a lv shunt borstreconstructie Echocardiography is the mainstay of the diagnosis and helpful in differentiating this entity from .
The only requirement to actually take the mission is easy too, 3 blades with level 1 Agronomy. So basically, keep any water or wind blades that have that field skill and your golden. Fulfilling the bonus requirements (+3 wind mastery, +3 water mastery) makes the missing take 11:36 minutes.
0 · Radboudumc borstreconstructie LV shunt
1 · Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
2 · Multimodality Imaging of a Gerbode Defect
3 · LV
4 · Intermediate type of Gerbode defect: rare type of the left to right
5 · Image Fusion Guided Device Closure of Left Ventricle to Right
6 · Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
7 · Acquired left ventricular–right atrium shunts
8 · Acquired Left Ventricle to Right Atrial Shunt (Gerbode Defect
9 · A Left Ventricular–to–Right Atrial Shunt in a Patient With a
Price: $170. Weight: 10.9 oz (M), 10.2 oz (W) Type: Trail. The right shoe for: Runners looking for a trail shoe that keeps wind and water out. BUY NOW MORE IMAGES. These high-tops aren’t.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators . LV-RA Shunt. Shunt from left ventricle through the VSD across the fenestration in septal leaflet of tricuspid valve into the right atrium. A shunt from the left ventricle to the right atrium.Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance. Review the transition . Dr. Gerbode first described a left ventricle (LV) to right atrial (RA) shunt in 1958. .
A transesophageal echocardiogram confirmed the presence of an LV to RA shunt .Echocardiography is the mainstay of the diagnosis and helpful in differentiating this entity from .
Image fusion guided device closure of left ventricle to right atrium shunt. A, . A case of a perimembranous VSD with a left ventricular–to–right atrial (LV-to .Learning Objectives. Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance. . Symptoms of LV–RA shunts vary from asymptomatic to severe heart failure and .
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators .LV-RA Shunt. Shunt from left ventricle through the VSD across the fenestration in septal leaflet of tricuspid valve into the right atrium. A shunt from the left ventricle to the right atrium.Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance. Review the transition from fetal to mature circulation. Determine the effects of the transitional circulation on the physiology of left to right shunts. Correlate clinical signs and symptoms with cardiac physiology.Dr. Gerbode first described a left ventricle (LV) to right atrial (RA) shunt in 1958. These defects are usually congenital, but cases of acquired defects secondary to aortic or tricuspid valve endocarditis have been described.
A transesophageal echocardiogram confirmed the presence of an LV to RA shunt consistent with a Gerbode defect (Figure 1 B and 1 C). To further define shunt anatomy and to quantify the shunt ratio, cardiac MRI was performed.
Radboudumc borstreconstructie LV shunt

Pathophysiology: Left To Right Shunts
Echocardiography is the mainstay of the diagnosis and helpful in differentiating this entity from the ruptured sinus of Valsalva into the RA (continuous shunt), endocardial cushion defect, VSD with TR. There is a significant gradient from LV to RA shunt on Doppler interrogation. Image fusion guided device closure of left ventricle to right atrium shunt. A, Preintervention transthoracic echocardiogram, 4-chamber view in color-compare mode showing left ventricle to right atrium (LV-RA) shunt (white arrow).

A case of a perimembranous VSD with a left ventricular–to–right atrial (LV-to-RA) shunt, which was misinterpreted as a tricuspid regurgitation (TR) jet on preoperative transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), is reported.
Learning Objectives. Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance. Review the transition from fetal to mature circulation. Correlate clinical signs and symptoms with cardiac physiology as it relates to left to right shunt lesions: VSD, PDA, ASD. Symptoms of LV–RA shunts vary from asymptomatic to severe heart failure and ultimately to death. The shunt from the high-pressure chamber (LV) to the low-pressure chamber (RA) easily overloads pulmonary circulation, causing congestion or oedema.About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators .
LV-RA Shunt. Shunt from left ventricle through the VSD across the fenestration in septal leaflet of tricuspid valve into the right atrium. A shunt from the left ventricle to the right atrium.Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance. Review the transition from fetal to mature circulation. Determine the effects of the transitional circulation on the physiology of left to right shunts. Correlate clinical signs and symptoms with cardiac physiology.Dr. Gerbode first described a left ventricle (LV) to right atrial (RA) shunt in 1958. These defects are usually congenital, but cases of acquired defects secondary to aortic or tricuspid valve endocarditis have been described.
A transesophageal echocardiogram confirmed the presence of an LV to RA shunt consistent with a Gerbode defect (Figure 1 B and 1 C). To further define shunt anatomy and to quantify the shunt ratio, cardiac MRI was performed.Echocardiography is the mainstay of the diagnosis and helpful in differentiating this entity from the ruptured sinus of Valsalva into the RA (continuous shunt), endocardial cushion defect, VSD with TR. There is a significant gradient from LV to RA shunt on Doppler interrogation. Image fusion guided device closure of left ventricle to right atrium shunt. A, Preintervention transthoracic echocardiogram, 4-chamber view in color-compare mode showing left ventricle to right atrium (LV-RA) shunt (white arrow).
A case of a perimembranous VSD with a left ventricular–to–right atrial (LV-to-RA) shunt, which was misinterpreted as a tricuspid regurgitation (TR) jet on preoperative transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), is reported.Learning Objectives. Learn the relationships between pressure, blood flow, and resistance. Review the transition from fetal to mature circulation. Correlate clinical signs and symptoms with cardiac physiology as it relates to left to right shunt lesions: VSD, PDA, ASD.

Multimodality Imaging of a Gerbode Defect

genuine rolex 5513 for sale as is
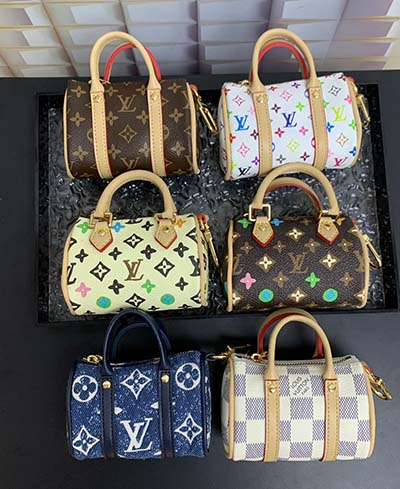
Supreme x Louis Vuitton isn't even on sale yet and it's already one of, if not the most hyped-up fashion collaboration of all-time. And that's not us being hyperbolic.
lv shunt borstreconstructie|A Left Ventricular–to–Right Atrial Shunt in a Patient With a